A transparent, strong plastic frequently used as a lightweight, break-resistant substitute for glass is Plexiglass or acrylic glass. Because of its adaptability, its significance cuts across several industries. Skylights and windows are made with it in the building. You’ll be able to choose Plexiglass for Safety and Design at the end of this article. Car windows and headlights are two places that can be found in the automotive sector.
Protective barriers and devices are utilized in the medical industry, and plexiglass is also highly prized in the arts for sculptures and display cases. Its strength, simplicity, and ease of shaping make it a popular choice across various fields. Learn more about its versatile applications here.
What is Plexiglass?

Plexiglass is an explicit, robust material that resembles glass but is far lighter and more resilient. Because it is more durable than glass, it is frequently utilized in its place. Choose Plexiglass for Safety and Design wisely. Plexiglass is used in windows, auto components, and safety barriers. Its safety, adaptability, and ease of shaping for many purposes make it a popular choice.
Properties of Plexiglass

- Due to its exceptional transparency, over 90% of light may travel through Plexiglass. Because it is lighter and more resilient than glass, it is an excellent substitute for glass in windows, displays, and lenses, offering clean, undistorted views.
- Plexiglass is substantially more rigid and impact-resistant than glass. Because it doesn’t break easily, it is safer for places like schools, hospitals, and public locations where breakage could be dangerous.
- Plexiglass weighs significantly less than glass. It is simpler to handle, transfer, and install because of this feature. It benefits applications requiring weight reduction, such as aircraft windows and signage.
- Plexiglass doesn’t turn yellow or deteriorate when exposed to extreme weather, including UV light. This makes it perfect for exterior applications where long-term clarity and durability are needed, such as skylights, greenhouses, and outdoor signage.
- Plexiglass is simple to drill, cut, and mold into various shapes. It is adaptable and may be thermoformed and molded into complicated shapes for multiple applications, including sophisticated industrial parts and artistic sculptures.
Manufacturing Process
Polymerization is the method used to create Plexiglass. This involves combining a catalyst with a liquid monomer and pouring the mixture into a mold. When the mixture is heated, the monomer solidifies into a solid plastic sheet or shape. After that, the completed Plexiglass is cooled, shaped, and polished to fit a variety of applications. So that’s why Plexiglass for Safety and Design is important to select wisely.
Applications of Plexiglass
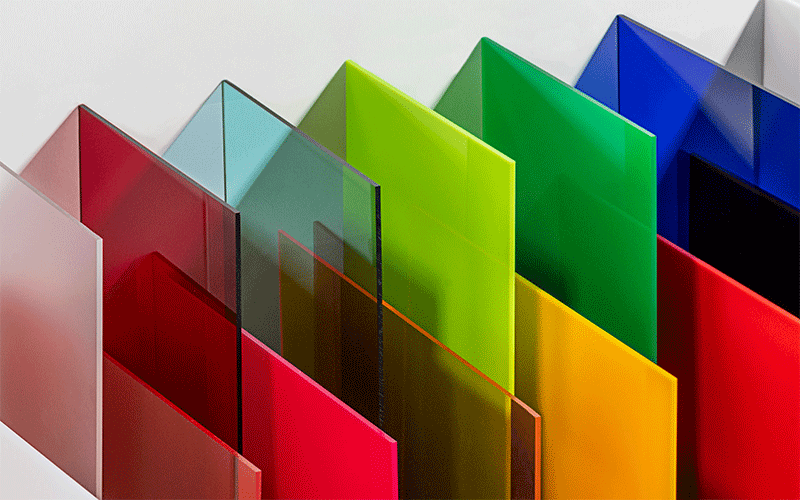

- Architecture & Construction: Because of its robustness and clarity, Plexiglass is utilized for windows, skylights, and facades. It is more impact-resistant than glass and lets in natural light, making buildings safer and more energy-efficient.
- Automotive Industry: Plexiglass is used for automobile headlight covers, sunroofs, and windows. Because it is lighter, it uses gasoline more efficiently, and because it is more durable, there is less chance of it breaking.
- Aerospace Applications: Plexiglass is used in cockpit canopies and aircraft windows because it is robust, lightweight, and resistant to high impacts and temperature changes, improving performance and safety.
Plexiglass is widely used for exhibition stands, showcases, and signage. Because of its superior clarity and simplicity of construction, it is perfect for product displays and eye-catching retail and museum exhibits.
Advantages of Plexiglass

- Lightweight Nature: Plexiglass is easier to handle, transport, and install than glass because it weighs significantly less. Particularly in construction and automotive applications, this lowers shipping costs and streamlines installation procedures.
- Flexibility in Shaping and Forming: Plexiglass is readily cranked, drilled, molded, and thermoformed into various forms and dimensions. Because it adapts to multiple requirements, its versatility enables creative ideas in product displays, art, and architecture.
- Improved Safety Features: Plexiglass resists impact better than glass, so it doesn’t break as quickly. This increases its safety when used in high-traffic public spaces, schools, and hospitals, where breaking could be a concern.
If you want to know more about Plexiglass and acrylic sheets, you can explore this detailed guide on acrylic sheets and their importance.
Disadvantages and Limitations
- Scratching and Cleaning Issues: Over time, scratches on Plexiglass may impair its clarity and attractiveness because it is more prone to scratches than glass. Abrasive materials and strong cleaners can harm surfaces. Thus, extra caution is essential; soft cleaning techniques and certain chemicals are needed.
- Cost considerations: Although Plexiglass has several advantages over other polymers, its price might often be higher. The increased cost may affect the entire project expense in projects that are sensitive to budget, particularly when large quantities are required.
- Vulnerability to Specific substances: Solvents and alcohols are two examples of substances that might harm polycarbonate glass. Its usage is restricted in settings where these chemicals are present because they can lead to cracking, clouding, or other types of degradation.
Conclusion
Plexiglass is a multipurpose, lightweight, and strong material extensively utilized in several sectors, such as aircraft, automotive, building, and protective barriers. Weather resistance, improved safety, and ease of shape are some of its main benefits. It does have some drawbacks, though, like being more expensive, prone to scratches, and sensitive to some chemicals. In the future, Plexiglass for Safety and Design will probably be used in more creative applications due to its versatility, the growing demand for transparent, safe materials in public areas, and the development of new technologies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’S)

What applications does Plexiglass frequently find in construction and architecture?
Plexiglass’s clarity and impact resistance make it a popular material for windows, skylights, and facades.
Why does the automotive industry prefer Plexiglass?
Plexiglass is favored because it is lightweight, which increases fuel efficiency, and durable, which lowers the chance of breaking and improves safety.
What are the benefits of Plexiglass for aerospace applications?
Plexiglass is a lightweight, robust material used in aerospace for airplane windows and cockpit canopies because it is resistant to heavy impacts and temperature changes.
What difficulties does cleaning Plexiglass present?
Plexiglass is easily scratched, so it needs to be cleaned carefully and with special tools to prevent damage and preserve its clarity.
What is the main drawback of utilizing Plexiglass in terms of costs?
Due to its higher cost than other plastics, Plexiglass may only be affordable for projects requiring small amounts of material.
